DERMATOPHYTOSIS
Dermatophytosis, commonly known as ringworm, is a superficial fungal infection that affects the skin, hair, and nails. The condition is caused by dermatophytes, a group of fungi that thrive on keratin, the protein that makes up the outer layer of skin, hair, and nails. Dermatophytosis can occur in various parts of the body, leading to a range of clinical presentations, each commonly referred to by different names depending on the affected area. Despite its name, ringworm is not caused by a worm but gets its name from the ring-like appearance of the rash.
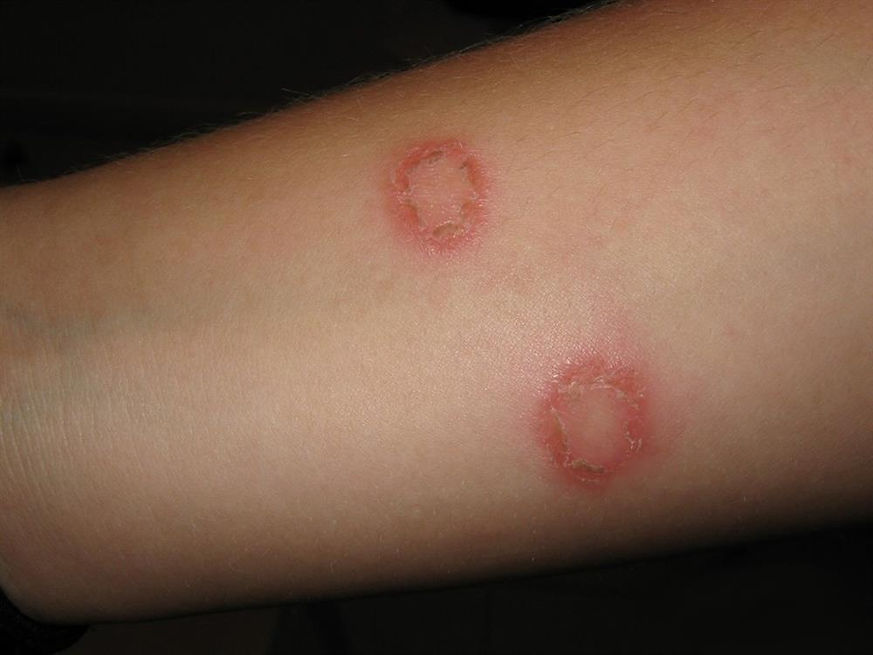
TYPES OF DERMATOPHYTOSIS
Tinea Capitis (Scalp Ringworm):
-
Overview: Tinea capitis is an infection of the scalp and hair shafts, primarily affecting children. It is highly contagious and can spread through direct contact with an infected person or contaminated objects like combs or hats.
-
Symptoms: Scaly patches on the scalp, hair loss, redness, itching, and sometimes swollen lymph nodes. Severe cases may lead to the formation of a kerion, a painful, inflammatory mass.
Causes: Fungi such as Trichophyton and Microsporum species are common culprits.
Tinea Corporis (Body Ringworm):
-
Overview: Tinea corporis affects the skin on the body, often presenting as round, red, and scaly patches with clear or less inflamed centres.
-
Symptoms: Circular, itchy, red patches that may spread to other parts of the body. The edges of these patches are usually raised and may blister.
-
Causes: Caused by several species of dermatophytes, including Trichophyton rubrum, Trichophyton mentagrophytes, and Microsporum canis.
Tinea Cruris (Jock Itch):
-
Overview: Tinea cruris affects the groin area and is more common in men than in women. It is often exacerbated by warm, moist environments and friction from clothing.
-
Symptoms: Red, itchy rash in the groin area, which may spread to the inner thighs and buttocks. The rash typically has a well-defined border and may blister or ooze.
-
Causes: Commonly caused by Trichophyton rubrum and Epidermophyton floccosum.
Tinea Pedis (Athlete's Foot):
-
Overview: Tinea pedis is a common infection of the feet, particularly between the toes. It thrives in warm, damp environments such as locker rooms and swimming pools.
-
Symptoms: Itching, burning, and stinging between the toes, dry and peeling skin, and in some cases, blistering or cracking of the skin.
-
Causes: Typically caused by Trichophyton rubrum and Trichophyton mentagrophytes.
Tinea Unguium (Onychomycosis):
-
Overview: Tinea unguium affects the nails, leading to thickening, discolouration, and separation of the nail from the nail bed. It is more common in toenails than fingernails.
-
Symptoms: Thickened, brittle, discoloured nails, often yellow or white. The nails may become deformed, and debris may accumulate under the nails.
-
Causes: Most commonly caused by Trichophyton rubrum.
Tinea Barbae:
-
Overview: Tinea barbae affects the beard and moustache areas of the face, primarily in adult men. It can be transmitted through direct contact with animals or humans.
-
Symptoms: Red, inflamed, and sometimes pustular lesions in the beard area, with associated hair loss.
-
Causes: Caused by Trichophyton and Microsporum species.
CAUSES AND TRANSMISSION OF DERMATOPHYTOSIS
Dermatophytosis is caused by dermatophytes, which are a group of fungi that include three genera: Trichophyton, Microsporum, and Epidermophyton. These fungi thrive in keratin-rich environments and can infect humans, animals, and even soil.
Transmission:
-
Direct Contact: Dermatophytosis is often spread through direct skin-to-skin contact with an infected person or animal.
-
Indirect Contact: It can also be transmitted through contact with contaminated objects such as clothing, towels, combs, or surfaces like floors in public showers.
-
Environmental Factors: Warm, humid environments promote the growth and spread of dermatophytes, making dermatophytosis more common in tropical and subtropical regions.
SYMPTOMS OF DERMATITIS
The symptoms of dermatophytosis vary depending on the affected area but commonly include:
-
Red, Scaly Patches: These patches may be circular with a clear centre, giving them a ring-like appearance.
-
Itching: Intense itching is a hallmark of dermatophytosis, which can lead to scratching and further skin irritation.
-
Blistering: In some cases, the affected area may develop blisters that ooze and crust over.
-
Hair Loss: When the scalp or beard is affected, hair loss can occur in the infected areas.
-
Thickened or Discoloured Nails: In tinea unguium, the nails may become thick, brittle, and discoloured, often yellow or white.

PREVENTION OF DERMATITIS
Preventing dermatophytosis involves reducing exposure to the fungi and maintaining good personal and environmental hygiene:
-
Practice Good Hygiene: Regularly wash and dry the skin, particularly after sweating. Change socks and underwear daily and avoid sharing personal items.
-
Use Protective Footwear: In communal showers or locker rooms, wear flip-flops or waterproof sandals to reduce the risk of tinea pedis.
-
Avoid Close Contact with Infected Individuals: Refrain from sharing clothing, towels, or bedding with someone who has a fungal infection.
-
Disinfect Contaminated Items: Clean and disinfect items like combs, brushes, and sports equipment that may be contaminated with dermatophytes.
-
Manage Environmental Factors: Control humidity in living spaces, and keep the skin dry, particularly in body folds prone to moisture buildup.













